CSL780: Computer Vision Introduction
First of all, three main terms are introduced - Image Processing, Computer Vision and Image Understanding.
Wherein IP (Image Processing) mainly deals with working on the pixels in the images, Computer Vision deals with working on features extracted. In Image Understanding comes the term SLAMP which refers to Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAMP) which is for 3D images.
Part 1: Image Processing
An example was given that, given 2 images of a person from different cameras, we can estimate the distance of the person from the cameras.
The discussion moved on to the resolution of HD vides, 720x1080 pixels, Full HD: 1920x1080. Also, any mobile having specification of greater than 320 ppi (pixels per inch) is not really useful as there will not be much difference.
The process of converting high resolution image to a lower resolution for example, 1920x1080 to 500x500 pixels is called downsampling.
Then, came Compression Techniques. An image of 1000x1000 resolution with 3 channels (RGB) will have 3 million pixels. Since 1 pixel = 8 bits, it will take around 24 mb = 3 mB. Any compression technique generally reduces this size of image.
jpeg is the most famous of these. It maintains something known as a quantisation table.
png performs lossless encoding.
A dark image is generally smooth and easy to compress.
A question was raised, why do 2 images taken from the same phone have different sizes? The answer was something like that the brightness condition and other focus state of camera, etc play a role in this.
Another one, why are raw images useful? They can be used in medical imaging (as we don’t want to lose any small piece of information) and even in satellite images.
Another, is decompression of image also possible? No, any lossy compression technique converted image cannot be decompressed.
Part 2: Computer Vision
Some terms like SURF (Speeded up Robust Features) and LBF (Local Best-Fit) were brought up since mainly CV involves feature extraction.
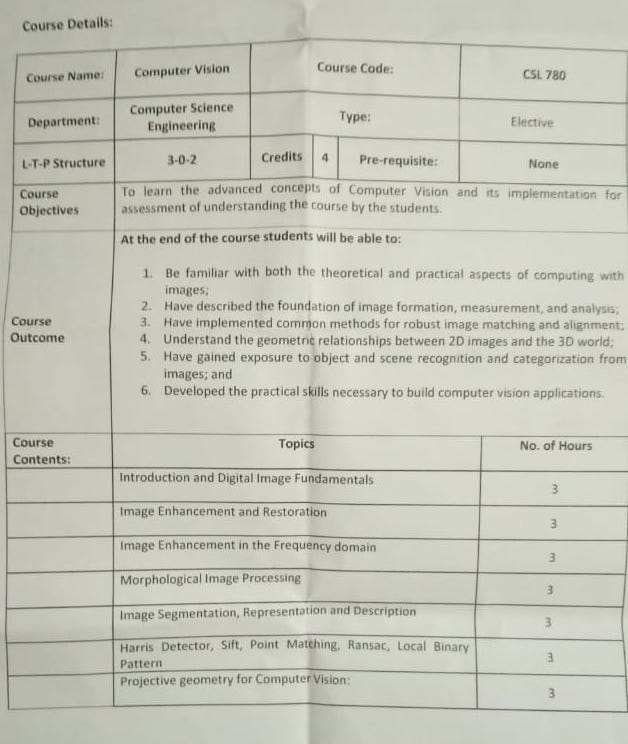
The following topics will be dealt in detail:
- Sampling and Quantization
- Image Enhancement
- Image Restoration (for e.g. getting colored image from a black & white image) - It can happen when we know the cause that distorted the image.
- Histogram Equalization
- Ransac Outlier Detection
- Projective Geometry for Computer Vision
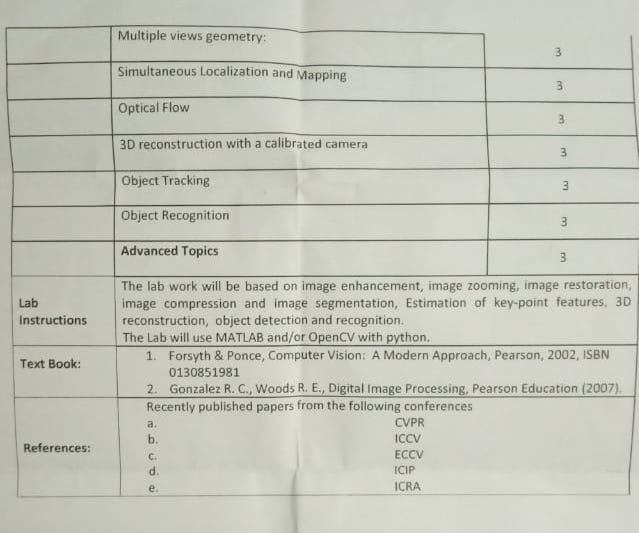
- Multiple View Geometry
Some terms like dead pixel came up. Any pixel that shows different behaviour than central pixel.
In tall buildings, GPS does not work, so Localization can be done using Projective Geometry. Here, SLAM comes into picture.
There are two main types of SLAM - ORB Slam and LSD SLAM.
Part 3: Image Understanding
Object recognition basics will be dealt. Object tracking can be included.
Research Papers:
The following conference papers are advised:
- CVPR
- ICCV
- ECCV
- ICIP
- ICRA
Course Logistics:
The course break up was given as:
- Minor 1 - 20 marks
- Minor 2 - 20 marks
- Major - 30 marks
- Two projects (open research problems) - 30 marks
All the exams will be open book.
Books recommended for the course are:
- Forsyth & Ponce, Computer Vision: A Modern Approach, Pearson, 2002
- Gonzalez R.C., Woods R.E., Digital Image Processing, Pearson Education (2007)